Understanding Room Temperature In Kelvin: A Comprehensive Guide
Room temperature in Kelvin is a crucial concept in various scientific fields, particularly in physics and chemistry. Understanding this measurement helps us grasp the fundamentals of thermodynamics and how temperature impacts different materials and processes. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the science behind everyday phenomena, this article will provide you with a thorough understanding of room temperature in Kelvin and its applications.
Temperature is one of the most fundamental physical properties we encounter daily. While most people are familiar with temperature scales like Celsius and Fahrenheit, the Kelvin scale offers a unique perspective, especially in scientific contexts. This article will delve into the intricacies of room temperature in Kelvin, explaining its significance, how it's measured, and why it's preferred in certain scenarios.
By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of room temperature in Kelvin, its practical applications, and how it compares to other temperature scales. Let's explore the fascinating world of thermodynamics and uncover the importance of this essential measurement.
Read also:Raymond Washington The Untold Story Of A Visionary Leader
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Room Temperature
- What is the Kelvin Scale?
- Converting Room Temperature to Kelvin
- Importance of Room Temperature in Kelvin
- Applications in Science and Industry
- Comparing Kelvin to Other Temperature Scales
- Room Temperature Standards and Variations
- Practical Examples of Room Temperature in Kelvin
- Common Misconceptions About Room Temperature
- Conclusion and Further Reading
Introduction to Room Temperature
Room temperature is a term commonly used to describe the ambient temperature in indoor environments. While it varies slightly depending on the location and season, it generally refers to temperatures that are comfortable for human habitation. The standard range for room temperature is typically between 20°C and 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
In scientific contexts, room temperature is often defined more precisely. For example, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines standard ambient temperature as 25°C (77°F). This standardization is crucial for conducting experiments and ensuring consistency across different studies and applications.
Understanding room temperature in Kelvin is essential because it provides a universal scale that is independent of arbitrary reference points like the freezing and boiling points of water. This makes it particularly useful in fields like thermodynamics, where absolute measurements are critical.
What is the Kelvin Scale?
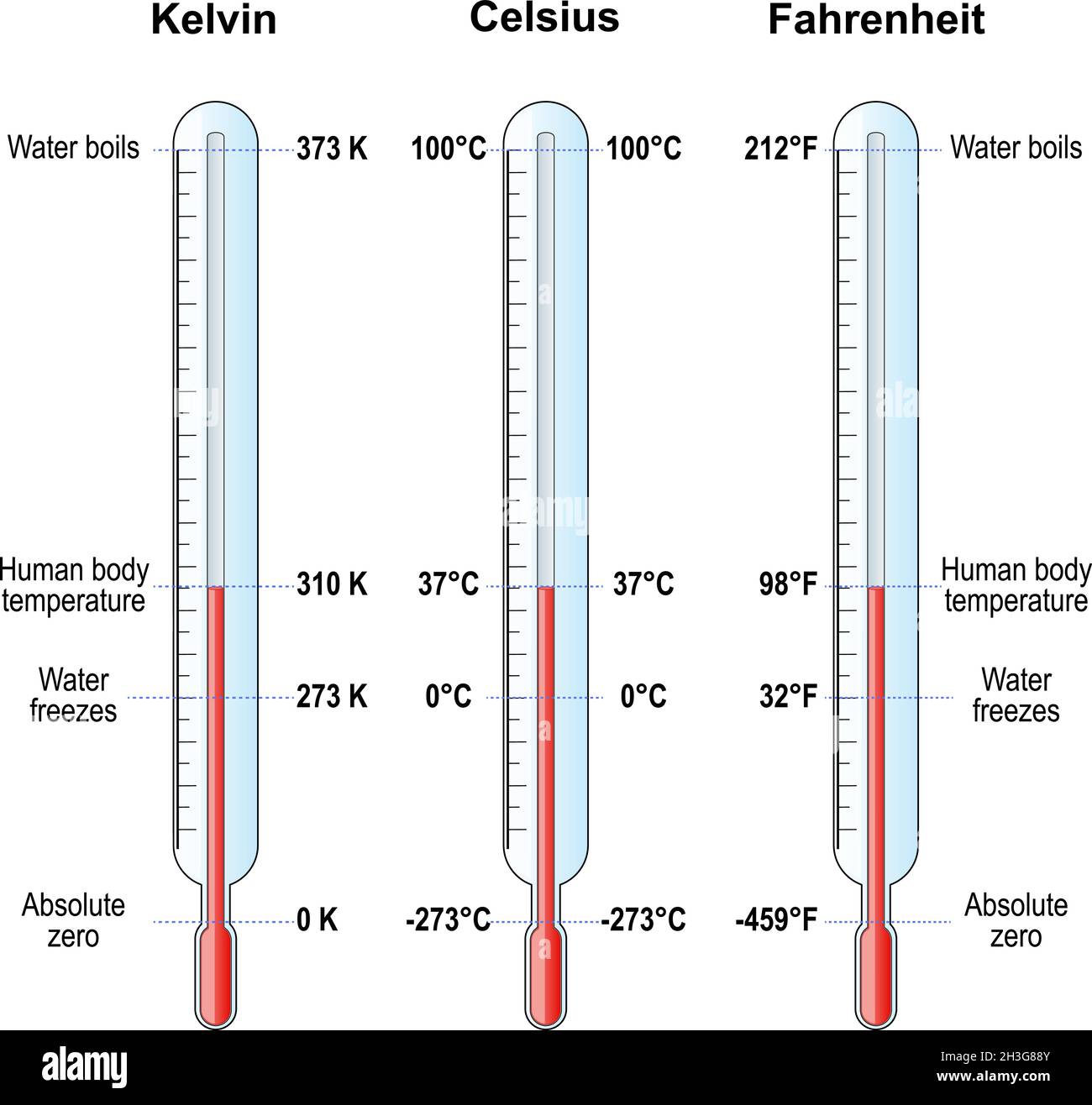
The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale used primarily in scientific contexts. Unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit, which are based on arbitrary reference points, the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. This makes it an ideal scale for scientific measurements and calculations.
Key Characteristics of the Kelvin Scale
- Absolute Zero: The Kelvin scale begins at absolute zero, which is equivalent to -273.15°C.
- No Negative Values: Since it starts at absolute zero, the Kelvin scale has no negative values, making it easier to work with in scientific equations.
- SI Unit: The Kelvin is the base unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI).
The Kelvin scale is particularly useful in fields like thermodynamics, astrophysics, and materials science, where precise temperature measurements are crucial. Its absolute nature allows scientists to make accurate predictions and calculations without the need for conversion or adjustment.
Converting Room Temperature to Kelvin
Converting room temperature from Celsius to Kelvin is a straightforward process. Since the Kelvin scale is based on absolute zero, the conversion involves adding 273.15 to the Celsius temperature. For example, if the room temperature is 25°C, the equivalent temperature in Kelvin is:
Read also:Exploring The Enigmatic World Of Summer Bishil Azula
25°C + 273.15 = 298.15 K
This simple conversion highlights the relationship between the two scales and underscores the importance of the Kelvin scale in scientific contexts. By using Kelvin, scientists can ensure consistency and accuracy in their measurements and calculations.
Why Use Kelvin for Room Temperature?
- Precision: The Kelvin scale provides precise and absolute measurements, which are essential for scientific accuracy.
- Universality: Since Kelvin is the SI unit of temperature, it is universally recognized and used in scientific research.
- Compatibility: Many scientific equations and formulas are designed to work with Kelvin, making it the preferred scale in these contexts.
Importance of Room Temperature in Kelvin
Room temperature in Kelvin plays a vital role in various scientific and industrial applications. Its absolute nature makes it particularly useful in fields where precise temperature measurements are critical. Here are some key reasons why understanding room temperature in Kelvin is important:
Thermodynamic Calculations
In thermodynamics, temperature is a fundamental variable that affects the behavior of gases, liquids, and solids. The Kelvin scale's absolute nature allows scientists to make accurate predictions about how materials will behave under different conditions. For example, the ideal gas law, which relates pressure, volume, and temperature, is expressed using Kelvin.
Material Science
In material science, understanding room temperature in Kelvin is crucial for studying the properties of materials. Many materials exhibit different behaviors at different temperatures, and precise measurements are necessary to ensure accuracy in research and development.
Chemical Reactions
Temperature plays a critical role in chemical reactions, influencing reaction rates and equilibrium. By using the Kelvin scale, chemists can ensure consistency and accuracy in their experiments, leading to more reliable results.
Applications in Science and Industry
Room temperature in Kelvin has numerous applications across various fields, from scientific research to industrial processes. Here are some examples of how this measurement is used in practice:
Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, room temperature in Kelvin is used to study the behavior of materials and systems under normal conditions. This is particularly important in fields like electronics, where temperature can affect the performance of components.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, precise temperature control is essential for ensuring the stability and efficacy of drugs. Room temperature in Kelvin provides a standardized measurement that can be used to maintain consistent conditions during production and storage.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, temperature control is critical for ensuring safety and quality. Room temperature in Kelvin is used to monitor and maintain optimal conditions for storage and processing.
Comparing Kelvin to Other Temperature Scales
While the Kelvin scale is widely used in scientific contexts, it's important to understand how it compares to other temperature scales like Celsius and Fahrenheit. Here's a brief comparison of these scales:
Celsius vs. Kelvin
- Reference Points: Celsius is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, while Kelvin is based on absolute zero.
- Conversion: To convert Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273.15.
- Usage: Celsius is commonly used in everyday contexts, while Kelvin is preferred in scientific applications.
Fahrenheit vs. Kelvin
- Reference Points: Fahrenheit is based on the freezing point of a saltwater solution and the average human body temperature, while Kelvin is based on absolute zero.
- Conversion: To convert Fahrenheit to Kelvin, first convert to Celsius using the formula (°F - 32) × 5/9, then add 273.15.
- Usage: Fahrenheit is primarily used in the United States, while Kelvin is used globally in scientific contexts.
Room Temperature Standards and Variations
While room temperature is generally defined as 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), there are variations depending on the context and location. Here are some common standards and variations:
Standard Ambient Temperature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines standard ambient temperature as 25°C (77°F), which is equivalent to 298.15 K. This standard is widely used in scientific research and experiments.
Variations by Region
In different regions, room temperature may vary slightly due to climate and cultural preferences. For example, in warmer climates, room temperature may be closer to 25°C, while in cooler climates, it may be closer to 20°C.
Variations by Application
In certain applications, such as laboratories or industrial settings, room temperature may be more precisely controlled to ensure consistency and accuracy. This is particularly important in fields like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Practical Examples of Room Temperature in Kelvin
Understanding room temperature in Kelvin can be applied to various real-world scenarios. Here are some practical examples:
Thermometers and Temperature Sensors
Many modern thermometers and temperature sensors are calibrated to measure temperature in Kelvin. This is particularly useful in scientific and industrial applications where precise measurements are required.
Climate Control Systems
In climate control systems, room temperature in Kelvin can be used to monitor and adjust the temperature to maintain optimal conditions. This is important in settings like laboratories, hospitals, and data centers.
Research and Development
In research and development, room temperature in Kelvin is used to study the properties of materials and systems under controlled conditions. This is crucial for ensuring accuracy and reliability in experiments.
Common Misconceptions About Room Temperature
Despite its widespread use, there are several misconceptions about room temperature and its measurement in Kelvin. Here are some common misconceptions and the truth behind them:
Misconception: Room Temperature is Always 25°C
While 25°C is a standard reference point, room temperature can vary depending on the context and location. It's important to consider these variations when conducting experiments or making measurements.
Misconception: Kelvin is Only Used in Science
While the Kelvin scale is widely used in scientific contexts, it also has practical applications in industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and food processing. Its absolute nature makes it a valuable tool in these fields.
Misconception: Room Temperature is Constant
Room temperature can fluctuate due to factors like climate, season, and human activity. It's important to monitor and adjust temperature as needed to maintain optimal conditions.
Conclusion and Further Reading
In conclusion, understanding room temperature in Kelvin is essential for anyone involved in scientific research, industrial applications, or simply curious about the science behind everyday phenomena. The Kelvin scale's absolute nature and universality make it a valuable tool for ensuring accuracy and consistency in temperature measurements.
By exploring the various aspects of room temperature in Kelvin, we've uncovered its significance in thermodynamics, material science, and chemical reactions. We've also examined its applications in fields like physics, engineering, and pharmaceuticals, highlighting its versatility and importance.
If you found this article informative, we encourage you to share it with others who might benefit from this knowledge. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of temperature and its various scales.
For further reading, consider exploring topics like thermodynamics, the history of temperature scales, and the practical applications of Kelvin in modern science and industry. These resources will provide you with a broader perspective and enhance your appreciation for the fascinating world of temperature measurement.
What Is The Minimum Hiring Age At Chick-fil-A?
Are Mikasa And Levi Siblings? Unraveling The Truth Behind The Speculation
Allotta Fagina: The Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Mastering This Concept

Room Temperature In Kelvin Bruin Blog
Kelvin Temperature