Understanding Monomer Lipids: A Comprehensive Guide
Monomer lipids are essential building blocks in the formation of complex lipid structures, playing a crucial role in biological systems. These molecules are not only vital for energy storage but also serve as key components in cell membranes and signaling pathways. Understanding the structure and function of monomer lipids is fundamental to grasping how lipids contribute to various physiological processes. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about monomer lipids, their types, functions, and significance in biological systems.
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Among these, monomer lipids are the simplest form, serving as the foundational units for more complex lipid molecules. The study of monomer lipids is essential for understanding their role in health and disease. From energy metabolism to cell membrane integrity, these molecules influence numerous biological processes.
Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply someone interested in biochemistry, this article will provide you with a detailed and comprehensive overview of monomer lipids. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of what monomer lipids are, their biological importance, and how they contribute to maintaining life. Let's dive into the world of monomer lipids and uncover their fascinating properties and functions.
Read also:How Many Movies Of Doraemon Are There A Comprehensive Guide
- What Are Monomer Lipids?
- Types of Monomer Lipids
- Structure and Properties of Monomer Lipids
- Biological Functions of Monomer Lipids
- Role in Lipid Metabolism
- Health Implications of Monomer Lipids
- Applications in Industry
- Current Research and Developments
- Future Perspectives on Monomer Lipids
- Conclusion
What Are Monomer Lipids?
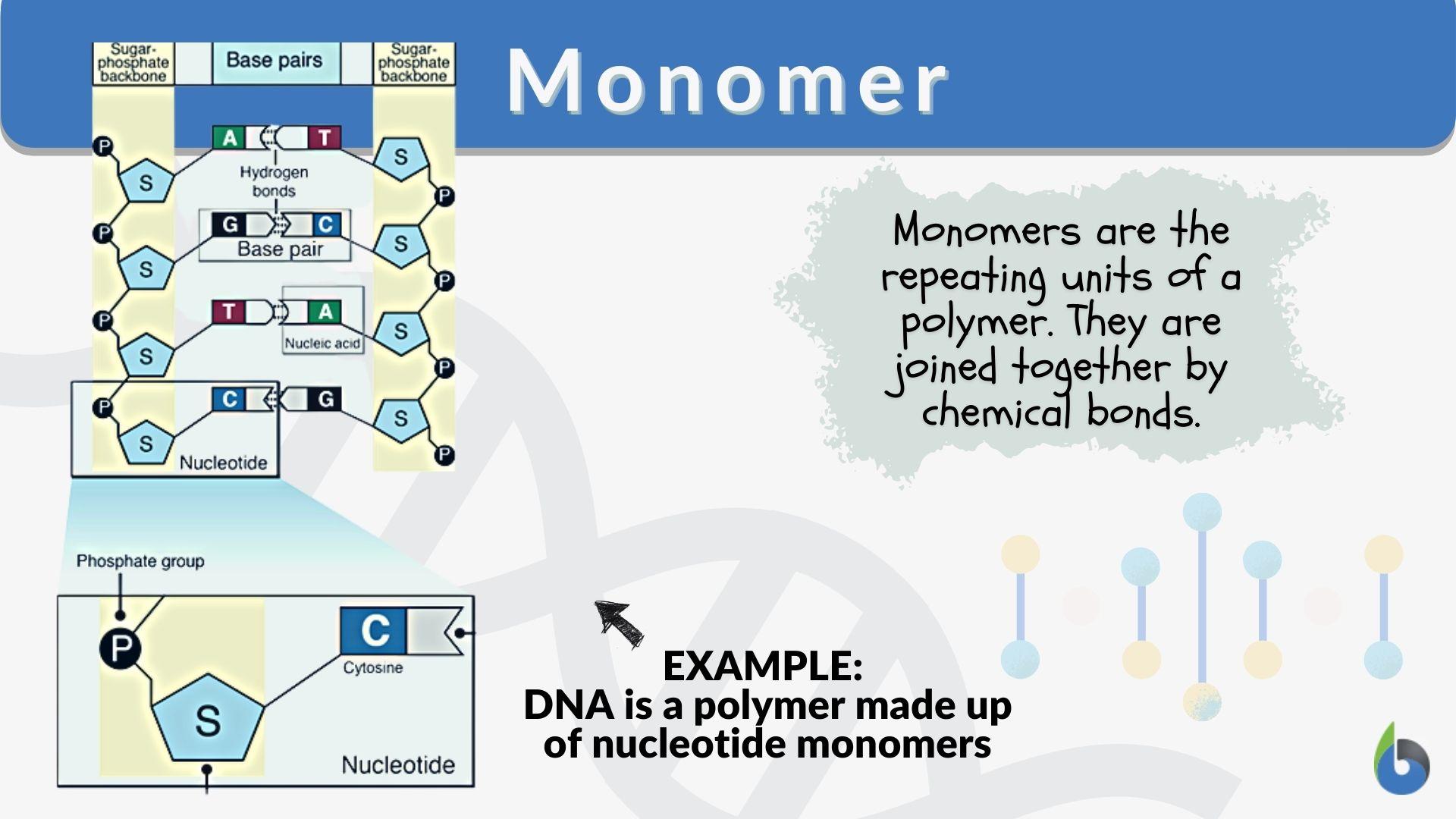
Monomer lipids are the simplest forms of lipids, often referred to as the building blocks of more complex lipid structures. These molecules consist of a glycerol backbone and one or more fatty acid chains. Unlike polymers, which are composed of repeating units, monomer lipids are single units that can combine to form larger molecules such as triglycerides, phospholipids, and glycolipids.
Monomer lipids are classified based on their chemical structure and functional groups. The most common type is fatty acids, which are long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group at one end. These fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated, depending on the presence of double bonds in their structure. Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fatty acids are typically liquid.
The diversity of monomer lipids allows them to perform a wide range of functions in biological systems. From serving as energy reserves to forming structural components of cell membranes, these molecules are indispensable for life. Understanding their basic structure and classification is the first step in appreciating their broader roles in health and disease.
Types of Monomer Lipids
Monomer lipids can be categorized into several types based on their chemical composition and functional groups. Below are the main types of monomer lipids:
- Fatty Acids: These are the most common type of monomer lipids, consisting of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. They can be saturated or unsaturated.
- Glycerol: A three-carbon alcohol that serves as the backbone for many lipid molecules, including triglycerides and phospholipids.
- Sphingosine: A long-chain amino alcohol that forms the backbone of sphingolipids, a class of lipids found in cell membranes.
- Cholesterol: A sterol lipid that plays a crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and serving as a precursor for steroid hormones.
Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are the primary type of monomer lipids and are characterized by their hydrophobic nature. They are classified into two main categories:
- Saturated Fatty Acids: These fatty acids lack double bonds in their hydrocarbon chain, making them solid at room temperature. Examples include palmitic acid and stearic acid.
- Unsaturated Fatty Acids: These contain one or more double bonds, making them liquid at room temperature. Examples include oleic acid and linoleic acid.
The presence of double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids introduces kinks in the hydrocarbon chain, preventing them from packing tightly. This property contributes to their liquid state and is crucial for maintaining membrane fluidity.
Read also:Doraemon The Beloved Anime Character That Captivates Generations
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple three-carbon alcohol that serves as the backbone for many lipid molecules. When combined with fatty acids, it forms triglycerides, which are the primary form of stored energy in the body. Glycerol is also a key component of phospholipids, which are essential for forming cell membranes.
Structure and Properties of Monomer Lipids
The structure of monomer lipids is defined by their hydrophobic and amphipathic properties. These properties are crucial for their biological functions and interactions within the body.
Monomer lipids are primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The hydrocarbon chains in fatty acids are hydrophobic, meaning they repel water. This property allows lipids to serve as effective barriers in cell membranes, preventing the passage of water-soluble molecules.
In addition to their hydrophobic nature, some monomer lipids, such as phospholipids, are amphipathic. This means they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. The hydrophilic head interacts with water, while the hydrophobic tail repels it. This unique structure allows phospholipids to form bilayers, which are the foundation of cell membranes.
Biological Functions of Monomer Lipids
Monomer lipids perform a variety of essential functions in biological systems. Below are some of the key roles they play:
- Energy Storage: Triglycerides, formed from monomer lipids, are the primary form of stored energy in the body. They provide a concentrated source of energy when broken down.
- Cell Membrane Structure: Phospholipids, derived from monomer lipids, form the structural framework of cell membranes, regulating the passage of molecules in and out of cells.
- Signaling Molecules: Some monomer lipids, such as fatty acids, serve as signaling molecules that regulate various physiological processes.
Energy Storage
Triglycerides, composed of glycerol and three fatty acids, are the primary form of stored energy in adipose tissue. When the body requires energy, triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, which are then metabolized to produce ATP.
Role in Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism involves the synthesis and breakdown of lipids to meet the body's energy needs. Monomer lipids play a central role in this process, as they are the building blocks of triglycerides and other complex lipids.
The breakdown of triglycerides into monomer lipids occurs through a process called lipolysis. This process releases fatty acids and glycerol, which can be used for energy production. Conversely, fatty acids and glycerol can be reassembled into triglycerides for storage during periods of energy surplus.
Health Implications of Monomer Lipids
The balance of monomer lipids in the body is crucial for maintaining health. Excessive intake of saturated fatty acids has been linked to cardiovascular diseases, while unsaturated fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are beneficial for heart health.
Understanding the role of monomer lipids in health and disease can help guide dietary choices and lifestyle modifications. For example, replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats in the diet can reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall health.
Applications in Industry
Monomer lipids have a wide range of applications in the food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries. They are used as emulsifiers, stabilizers, and thickening agents in food products. In cosmetics, they serve as moisturizers and emollients, improving skin hydration and texture.
In the pharmaceutical industry, monomer lipids are used in the formulation of drug delivery systems, such as liposomes. These systems enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of drugs by improving their absorption and distribution in the body.
Current Research and Developments
Recent advancements in lipid research have focused on understanding the role of monomer lipids in health and disease. Scientists are exploring the potential of monomer lipids as therapeutic agents for conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Emerging technologies, such as lipidomics, are enabling researchers to study the composition and function of lipids in greater detail. This field holds promise for identifying new biomarkers and developing targeted therapies for lipid-related disorders.
Future Perspectives on Monomer Lipids
The future of monomer lipid research is bright, with ongoing studies aimed at unlocking their full potential. As our understanding of lipid biology continues to evolve, new applications and therapies are likely to emerge.
One area of interest is the development of synthetic monomer lipids for use in drug delivery and tissue engineering. These lipids could be designed to target specific cells or tissues, improving the precision and efficacy of treatments.
Conclusion
Monomer lipids are essential molecules that play a vital role in biological systems. From energy storage to cell membrane structure, these building blocks are indispensable for life. Understanding their structure, function, and significance is crucial for advancing our knowledge of health and disease.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights on monomer lipids in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this knowledge. For more in-depth articles on biochemistry and related topics, be sure to explore our website.
Understanding The Biological Classification System: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, And Order
Nerve Ending Meme: The Hilarious Trend Taking The Internet By Storm
The Ultimate Guide To Mandrill In The Lion King: Symbolism, Facts, And Cultural Impact
Monomer Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

Styrene Monomer & Wax 500ml