Understanding Light Dependent Reactions: The Key To Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is one of the most vital processes on Earth, and light dependent reactions are at its core. These reactions are the first stage of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy. Understanding how light dependent reactions work is essential not only for students of biology but also for anyone interested in the science behind life on our planet. This article delves deep into the mechanisms, importance, and applications of light dependent reactions, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of this critical biological process.
Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve a series of steps that harness sunlight to produce energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH. These molecules are then used in the second stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin cycle, to synthesize glucose. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear picture of how this process works and why it’s so crucial for life as we know it.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of light dependent reactions, breaking down each step and explaining the science behind them. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or just a curious reader, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the world of photosynthesis. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets of light dependent reactions!
Read also:Brandy And Billy Youtube Unveiling The Journey Of A Viral Sensation
Table of Contents
What Are Light Dependent Reactions?
Light dependent reactions are the first phase of photosynthesis, occurring in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. These reactions are called "light dependent" because they require sunlight to function. The primary goal of this process is to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the subsequent Calvin cycle.
During these reactions, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments, exciting electrons to higher energy states. These high-energy electrons are then transferred through a series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane, known as the electron transport chain. This transfer of electrons drives the production of ATP and NADPH, which are later used to synthesize glucose.
The Role of Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment responsible for capturing light energy during light dependent reactions. It is located in the thylakoid membranes and plays a crucial role in absorbing photons from sunlight. Chlorophyll primarily absorbs light in the blue and red wavelengths, reflecting green light, which is why plants appear green.
There are two types of chlorophyll involved in light dependent reactions: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Chlorophyll a is the main pigment that participates directly in the light reactions, while chlorophyll b assists by expanding the range of light wavelengths a plant can use. Together, these pigments ensure that plants can efficiently capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
Steps of Light Dependent Reactions
Light dependent reactions involve a series of steps that work together to convert light energy into chemical energy. Below are the key stages of this process:
1. Light Absorption
When sunlight strikes the chlorophyll molecules in the thylakoid membranes, electrons in the chlorophyll become excited to higher energy levels. This is the first step in harnessing light energy.
Read also:Where To Watch Doraemon Movies In Hindi For Free A Complete Guide
2. Electron Excitation
Excited electrons are transferred to the primary electron acceptor, initiating the flow of electrons through the electron transport chain.
3. Photolysis of Water
Water molecules are split into oxygen, protons, and electrons. This process, known as photolysis, replenishes the electrons lost by chlorophyll and releases oxygen as a byproduct.
Photolysis of Water
Photolysis of water is a critical step in light dependent reactions. During this process, water molecules are split into oxygen, protons, and electrons. The oxygen is released as a byproduct, while the protons and electrons are used to drive the production of ATP and NADPH.
This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme complex called photosystem II (PSII). PSII absorbs light energy, which excites electrons and allows them to be transferred to the electron transport chain. The splitting of water ensures a continuous supply of electrons, maintaining the flow of energy through the system.
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes embedded in the thylakoid membrane. It facilitates the transfer of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I, driving the production of ATP and NADPH.
As electrons move through the ETC, they lose energy, which is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane. This creates a proton gradient, which is later used by ATP synthase to produce ATP. The final electron acceptor in the chain is NADP+, which is reduced to NADPH.
Production of ATP and NADPH
The ultimate goal of light dependent reactions is to produce ATP and NADPH. ATP is generated through a process called chemiosmosis, where protons flow back into the stroma through ATP synthase, driving the synthesis of ATP. NADPH is produced when NADP+ accepts electrons and protons at the end of the electron transport chain.
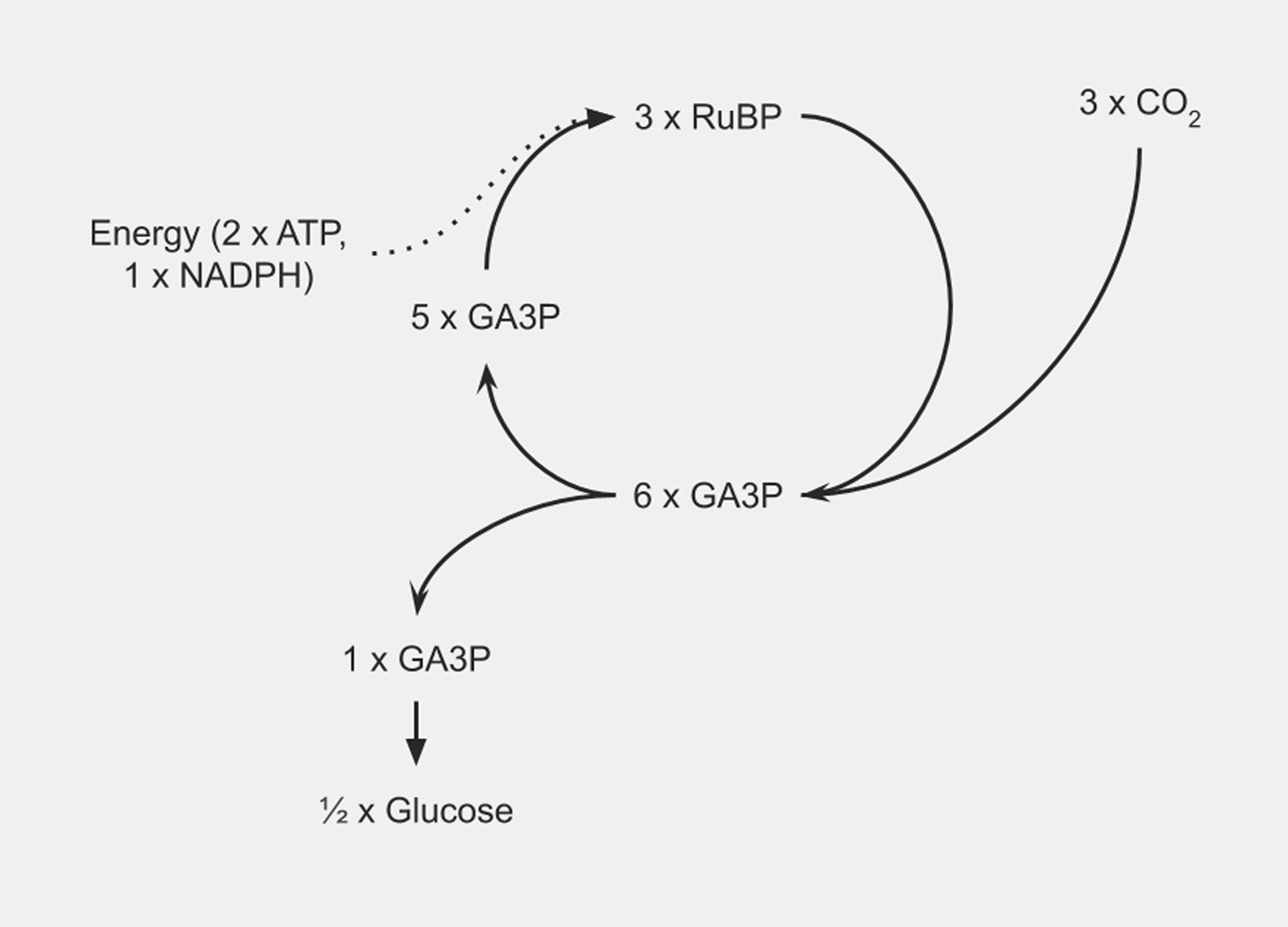
These energy-rich molecules are then transported to the Calvin cycle, where they are used to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide. Without ATP and NADPH, the Calvin cycle cannot proceed, highlighting the importance of light dependent reactions in photosynthesis.
Importance in Photosynthesis
Light dependent reactions are essential for photosynthesis because they provide the energy and reducing power needed for the Calvin cycle. Without these reactions, plants would not be able to convert carbon dioxide into glucose, the primary source of energy for most living organisms.
Additionally, light dependent reactions are responsible for producing oxygen, which is vital for aerobic respiration in animals and humans. This process underscores the interconnectedness of life on Earth and the critical role plants play in maintaining the planet’s ecosystems.
Applications and Research
Understanding light dependent reactions has practical applications in fields such as agriculture and renewable energy. For example, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis in crops to increase yields and address food security challenges.
In the field of renewable energy, scientists are studying artificial photosynthesis to develop technologies that mimic light dependent reactions. These technologies could potentially produce clean energy by converting sunlight into chemical fuels.
Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about light dependent reactions that are worth addressing:
- Misconception 1: Light dependent reactions only occur during the day. While they require sunlight, some organisms can adapt to low-light conditions.
- Misconception 2: Chlorophyll is the only pigment involved. In reality, accessory pigments like carotenoids also play a role.
- Misconception 3: The process is 100% efficient. In truth, some energy is lost as heat during electron transfer.
Conclusion
Light dependent reactions are a fascinating and essential part of photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy to fuel life on Earth. By understanding the steps involved, the role of chlorophyll, and the production of ATP and NADPH, we gain valuable insights into the science of biology and the interconnectedness of ecosystems.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below or explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of photosynthesis and related topics. Together, let’s continue to learn and appreciate the wonders of the natural world!
Can I Take Ibuprofen And Amoxicillin At The Same Time? A Comprehensive Guide
Discover Jeana Star: The Rising Social Media Sensation
Sonora Quest Lab Tests: Comprehensive Guide To Diagnostic Services
T 1.02 Lightdependent Reactions Barista Hustle

Light Dependent Reactions Worksheet