Comprehensive Guide To Back Muscle Names: Anatomy, Function, And Importance
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding back muscle names and their functions is crucial for maintaining overall physical health and preventing injuries. The back is one of the most complex parts of the human body, housing a network of muscles that support posture, movement, and stability. Whether you're an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone dealing with back pain, knowing the names and roles of these muscles can empower you to take better care of your body. This article will provide a detailed exploration of back muscle anatomy, their functions, and tips for maintaining a healthy back.
The back muscles are divided into several layers, each with unique roles and responsibilities. From superficial muscles that control large movements to deep muscles that stabilize the spine, every muscle group plays a vital role in daily activities. By learning the names and functions of these muscles, you can better understand how your body works and how to address issues like back pain or muscle imbalances.
This guide is designed to be a comprehensive resource for anyone interested in back muscle anatomy. We'll cover everything from the major muscle groups to specific exercises that can help strengthen these muscles. Whether you're looking to improve your posture, enhance athletic performance, or simply learn more about your body, this article will provide valuable insights.
Read also:When Was Doraemon Invented A Comprehensive Guide To The Beloved Robot Cat
Overview of Back Muscles
The back muscles are a complex network of tissues that work together to support the spine, enable movement, and maintain posture. These muscles are categorized into two main layers: superficial and deep. The superficial muscles are located closer to the skin and are primarily responsible for larger movements, such as bending and twisting. In contrast, the deep muscles are situated closer to the spine and play a key role in stabilizing the vertebrae and maintaining alignment.
Back muscle names can be intimidating at first glance, but they often provide clues about their location and function. For example, the "trapezius" muscle is named for its trapezoidal shape, while the "latissimus dorsi" refers to its wide, flat structure. Understanding these names can help you better visualize the muscles and their roles in the body. Additionally, knowing the back muscle names allows you to communicate more effectively with healthcare professionals if you experience pain or injury.
Before diving into the specifics, it's important to note that the back muscles are interconnected with other systems in the body, such as the nervous system and skeletal system. This interconnectedness means that issues in one area can affect the entire body. For example, weak back muscles can lead to poor posture, which may result in neck pain or headaches. Therefore, maintaining strong and healthy back muscles is essential for overall well-being.
Major Back Muscle Groups
The back muscles are divided into several groups, each with distinct functions. Below is an overview of the major back muscle groups and their roles:
- Trapezius: A large, triangular muscle that spans the upper back and neck. It helps with shoulder movement and stabilization.
- Latissimus Dorsi: Often referred to as the "lats," this muscle is responsible for pulling movements, such as rowing or climbing.
- Rhomboids: Located between the shoulder blades, these muscles help retract the scapula and maintain good posture.
- Erector Spinae: A group of muscles that run along the spine, providing support and enabling spinal extension.
- Quadratus Lumborum: A deep muscle in the lower back that aids in lateral flexion and stabilization of the spine.
These muscle groups work together to ensure smooth and coordinated movement. For example, the trapezius and rhomboids collaborate to stabilize the shoulder blades during lifting, while the latissimus dorsi and erector spinae work in tandem during activities like deadlifting. Understanding the synergy between these muscles can help you optimize your workouts and prevent injuries.
Additionally, the back muscles are closely linked to the core muscles, which include the abdominals and obliques. Together, these muscles form a "corset" that supports the spine and pelvis. Strengthening both the back and core muscles is essential for maintaining balance and preventing strain on any single muscle group.
Read also:Sonya Mcgaffey Age A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
Superficial Back Muscles
Trapezius
The trapezius is one of the most prominent back muscles, easily recognizable by its trapezoidal shape. It spans from the base of the skull to the middle of the back and extends laterally to the shoulder blades. The trapezius is divided into three sections: upper, middle, and lower. Each section has a unique function:
- Upper Trapezius: Elevates the shoulders and supports neck movement.
- Middle Trapezius: Retracts the scapula, bringing the shoulder blades closer together.
- Lower Trapezius: Depresses the shoulders and aids in scapular stabilization.
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi, or "lats," is the largest muscle in the back. It originates from the lower spine and pelvis and inserts into the upper arm. The primary functions of the latissimus dorsi include:
- Pulling the arms downward and backward.
- Assisting in internal rotation of the shoulder.
- Supporting posture during activities like standing or sitting.
Rhomboids
The rhomboids are located beneath the trapezius and are responsible for retracting the scapula. This action is essential for maintaining good posture and preventing rounded shoulders. Weak rhomboids can lead to muscle imbalances and discomfort in the upper back.
Deep Back Muscles
Erector Spinae
The erector spinae is a group of three muscles that run along the spine: the iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis. These muscles are crucial for spinal extension and maintaining an upright posture. They also help stabilize the spine during movement, reducing the risk of injury.
Quadratus Lumborum
The quadratus lumborum is a deep muscle located in the lower back. It plays a key role in lateral flexion of the spine and stabilizes the pelvis during walking or standing. Tightness in this muscle can contribute to lower back pain, making it important to stretch and strengthen it regularly.
Multifidus
The multifidus is a small but powerful muscle that spans the length of the spine. It provides segmental stability to each vertebra, ensuring smooth movement and reducing the risk of disc injuries. Strengthening the multifidus is often recommended for individuals recovering from back injuries.
Functions of Back Muscles
The back muscles perform a wide range of functions, from enabling movement to maintaining posture. Below are some of the key functions of back muscles:
- Movement: The back muscles are responsible for a variety of movements, including bending, twisting, lifting, and reaching.
- Posture: Strong back muscles help maintain an upright posture, reducing the risk of slouching and related discomfort.
- Stability: The deep back muscles, such as the multifidus and erector spinae, provide stability to the spine and pelvis.
- Breathing: Some back muscles, like the latissimus dorsi, assist in the breathing process by supporting the ribcage.
Understanding these functions can help you appreciate the importance of maintaining strong and healthy back muscles. For example, individuals who sit for long periods may experience weakened back muscles, leading to poor posture and discomfort. Incorporating exercises that target the back muscles can help counteract these effects and improve overall well-being.
Common Back Muscle Injuries
Back muscle injuries are a common issue, particularly among athletes and individuals with physically demanding jobs. Some of the most frequent back muscle injuries include:
- Strains: Overstretching or tearing of the back muscles, often caused by sudden movements or heavy lifting.
- Sprains: Injury to the ligaments that connect the back muscles to the bones.
- Herniated Discs: Although not a muscle injury, herniated discs can compress nearby muscles and nerves, causing pain and weakness.
Preventing back muscle injuries involves maintaining a balance between strength and flexibility. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises can help reduce the risk of strains and sprains. Additionally, using proper lifting techniques and avoiding repetitive motions can further protect the back muscles.
Strengthening Back Muscles
Strengthening the back muscles is essential for maintaining a healthy spine and preventing injuries. Below are some effective exercises for targeting the back muscles:
- Deadlifts: A compound exercise that engages the entire posterior chain, including the erector spinae and latissimus dorsi.
- Rows: Exercises like barbell rows and seated rows target the rhomboids and trapezius.
- Pull-Ups: A bodyweight exercise that strengthens the latissimus dorsi and upper back muscles.
- Bird-Dog: A stability exercise that targets the multifidus and other deep back muscles.
Incorporating these exercises into your routine can help build strength and resilience in the back muscles. It's important to start with lighter weights and focus on proper form to avoid injury. Additionally, combining strength training with flexibility exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, can enhance overall back health.
Importance of Back Muscle Health
Maintaining healthy back muscles is crucial for overall physical well-being. Strong and flexible back muscles contribute to better posture, reduced risk of injury, and improved athletic performance. Conversely, weak or imbalanced back muscles can lead to a host of issues, including chronic pain, poor posture, and decreased mobility.
Back muscle health is particularly important for individuals in YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) professions, such as healthcare workers, athletes, and manual laborers. These individuals rely on their back muscles to perform daily tasks and maintain their livelihoods. By prioritizing back muscle health, they can reduce the risk of injuries and improve their quality of life.
Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate rest are essential for maintaining healthy back muscles. Additionally, seeking professional guidance from a physical therapist or chiropractor can help address any underlying issues and prevent future problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding back muscle names and their functions is essential for maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. The back muscles play a vital role in movement, posture, and stability, making them a key focus for anyone looking to improve their physical health. By learning about the major back muscle groups, their functions, and how to strengthen them, you can take proactive steps toward preventing injuries and enhancing your overall well-being.
We encourage you to incorporate the exercises and tips outlined in this article into your routine. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced athlete, there's always room to improve your back muscle health. If you found this guide helpful, please consider sharing it with others or leaving a comment below. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles on muscle anatomy and fitness.
Dear Abby Uexpress: A Trusted Source For Life Advice And Guidance
Unlocking The Mysteries Of Angel Numbers 1313: Meaning, Significance, And Guidance
Queenie Sateen: A Comprehensive Guide To Luxurious Bedding
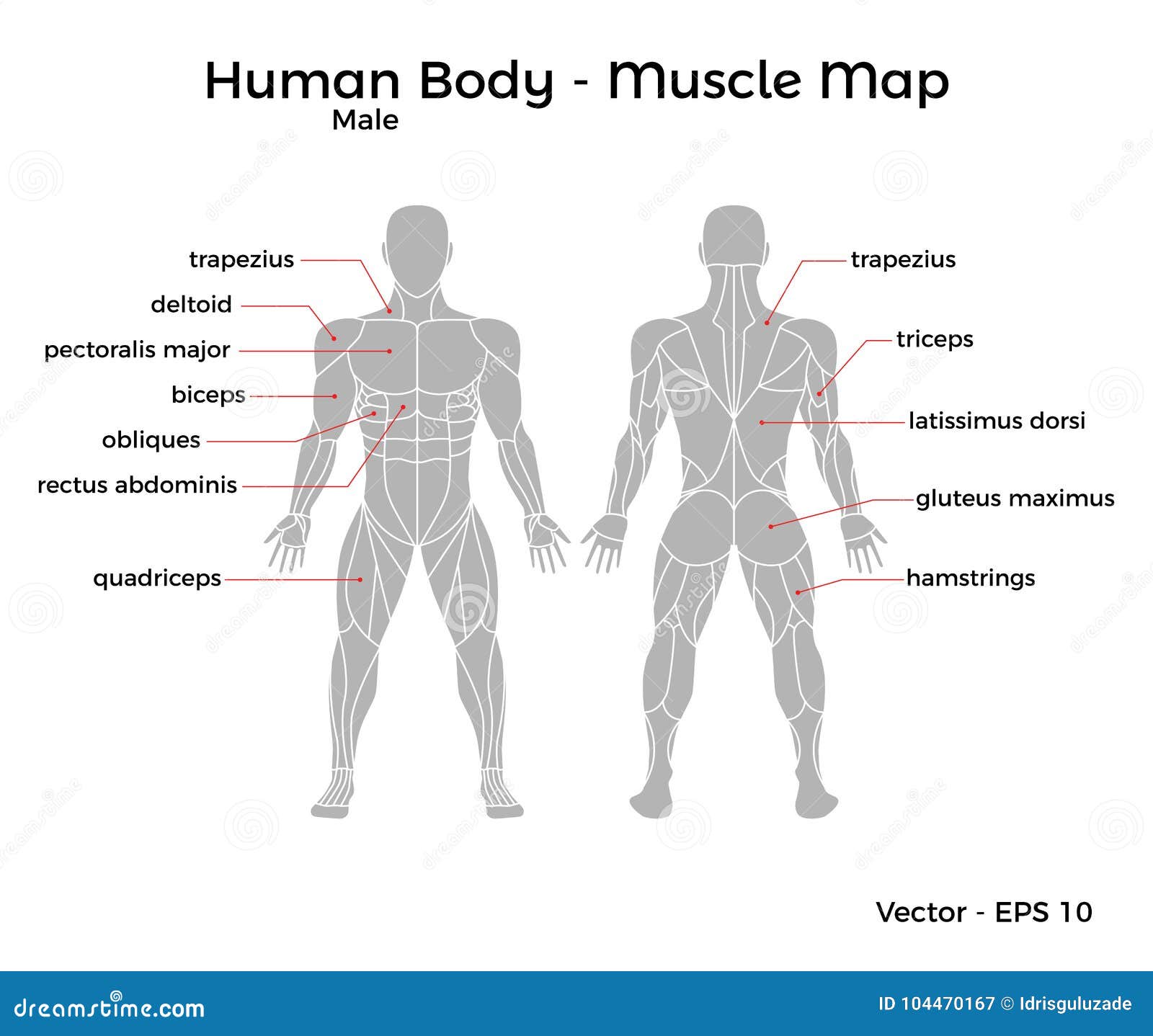
Male Human Body Muscle map stock vector. Illustration of body 104470167
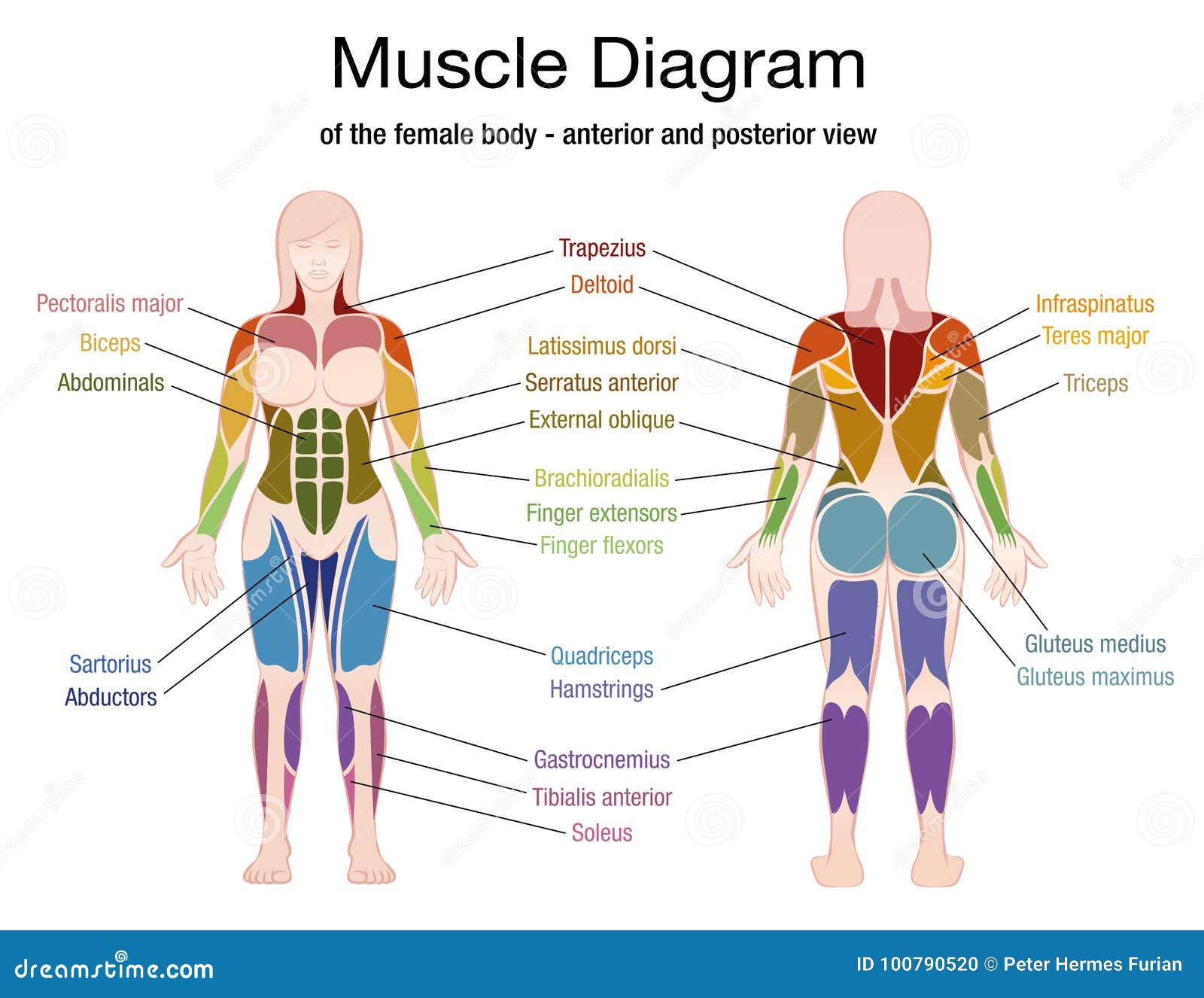
Muscle Diagram Female Body Names Stock Vector Illustration of colored