Understanding The Molar Mass Of CaCO3: A Comprehensive Guide
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is one of the most abundant compounds found in nature, playing a vital role in various industries and biological processes. Whether you're a student studying chemistry, a professional working in manufacturing, or someone curious about the science behind everyday materials, understanding the molar mass of CaCO3 is essential. This compound is commonly found in rocks, shells, and even dietary supplements, making it a cornerstone of both industrial and biological applications. In this article, we will explore the molar mass of CaCO3, its significance, and how it influences its properties and uses.
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. Its molar mass is a key property that helps scientists and engineers determine its behavior in chemical reactions and its role in various applications. The molar mass of CaCO3 is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent elements: calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). Understanding this concept is crucial for anyone working in fields such as pharmaceuticals, construction, or environmental science, where CaCO3 is frequently utilized.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the calculation of the molar mass of CaCO3, its chemical properties, and its wide-ranging applications. We will also discuss how this compound is used in industries such as agriculture, medicine, and manufacturing. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of CaCO3 and its importance in both scientific and practical contexts.
Read also:Fujiko F Fujio The Legendary Creator Behind Doraemon
Table of Contents
What is CaCO3?
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a chemical compound composed of calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). It is a white, odorless powder that occurs naturally in minerals such as calcite and aragonite. CaCO3 is found in rocks like limestone and marble, as well as in biological structures such as seashells and coral reefs. Its widespread presence in nature makes it an essential compound in various fields, including geology, biology, and industry.
Chemical Composition of CaCO3
CaCO3 consists of one calcium atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms. The chemical formula reflects the ratio of these elements in the compound. Its molecular structure gives it unique properties, such as its ability to react with acids to form carbon dioxide gas. This property is often utilized in applications such as antacid tablets and soil treatment.
Physical Properties of CaCO3
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Density: Approximately 2.71 g/cm³
- Melting Point: Decomposes at high temperatures
- Solubility: Low solubility in water but dissolves readily in acidic solutions
How to Calculate the Molar Mass of CaCO3
The molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in its chemical formula. For CaCO3, this involves calculating the atomic masses of calcium, carbon, and oxygen and adding them together.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the molar mass of CaCO3:
- Identify the atomic masses of the elements:
- Calcium (Ca): 40.08 g/mol
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Multiply the atomic mass of oxygen by 3, as there are three oxygen atoms in CaCO3.
- Add the atomic masses together:
- 40.08 (Ca) + 12.01 (C) + (16.00 × 3) (O) = 100.09 g/mol
The molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol.
Why Molar Mass Matters
The molar mass of CaCO3 is critical for stoichiometric calculations in chemistry. It allows scientists to determine the amount of CaCO3 required for a reaction or the quantity of products formed. For example, in the production of cement, knowing the molar mass of CaCO3 helps engineers calculate the precise amount of limestone needed.
Read also:Dekisugi Unveiling The Charismatic Protagonist Of Doraemon
Chemical Properties of CaCO3
CaCO3 exhibits several chemical properties that make it useful in various applications. One of its most notable characteristics is its reaction with acids, which produces carbon dioxide gas and water.
Reaction with Acids
When CaCO3 reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), the following reaction occurs:
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
This reaction is commonly used in laboratories to test for the presence of carbonate ions. It is also the basis for the use of CaCO3 in antacids, which neutralize stomach acid.
Thermal Decomposition
At high temperatures, CaCO3 undergoes thermal decomposition to form calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2):
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
This process, known as calcination, is used in the production of lime, a key material in construction and agriculture.
Applications of CaCO3
Calcium carbonate has a wide range of applications across various industries. Its versatility stems from its chemical and physical properties, as well as its abundance in nature.
Construction Industry
In the construction industry, CaCO3 is used as a raw material for producing cement and lime. It is also used as a filler in paints, plastics, and rubber to improve their properties.
Pharmaceuticals
CaCO3 is a common ingredient in antacid tablets and dietary supplements. It helps neutralize stomach acid and provides a source of calcium for bone health.
Environmental Applications
CaCO3 is used in water treatment processes to adjust pH levels and remove impurities. It is also employed in agriculture to improve soil quality and reduce acidity.
Industrial Uses of CaCO3
Calcium carbonate is a vital component in many industrial processes. Its role in manufacturing and production cannot be overstated.
Paper Industry
In the paper industry, CaCO3 is used as a filler and coating pigment to enhance the brightness and opacity of paper products.
Plastics and Rubber
CaCO3 is added to plastics and rubber to improve their mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and durability.
Biological Role of CaCO3
CaCO3 plays a crucial role in biological systems. It is a primary component of shells, bones, and teeth in many organisms.
Marine Life
Marine organisms such as corals and mollusks use CaCO3 to build their shells and exoskeletons. This compound provides structural support and protection.
Human Health
In humans, CaCO3 is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. It is also used as a dietary supplement to prevent calcium deficiency.
Environmental Impact of CaCO3
While CaCO3 is beneficial in many ways, its extraction and use can have environmental consequences.
Quarrying and Mining
The extraction of limestone, a primary source of CaCO3, can lead to habitat destruction and soil erosion. Sustainable practices are essential to minimize these impacts.
Carbon Emissions
The calcination process used to produce lime releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Safety Precautions When Handling CaCO3
While CaCO3 is generally safe, certain precautions should be taken when handling it in industrial or laboratory settings.
Dust Inhalation
Inhalation of CaCO3 dust can irritate the respiratory system. Proper ventilation and protective equipment are recommended.
Eye and Skin Contact
CaCO3 can cause mild irritation to the eyes and skin. Washing with water is advised if contact occurs.
Common Questions About CaCO3
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about calcium carbonate:
What is the molar mass of CaCO3?
The molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol.
Is CaCO3 soluble in water?
CaCO3 has low solubility in water but dissolves readily in acidic solutions.
What are the uses of CaCO3?
CaCO3 is used in construction, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and many other industries.
Conclusion
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a versatile and essential compound with a wide range of applications. Its molar mass, approximately 100.09 g/mol, is a key property that influences its behavior in chemical reactions and industrial processes. From its role in construction and pharmaceuticals to its importance in biological systems, CaCO3 is a cornerstone of modern science and industry.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CaCO3 and its significance. If you found this information helpful, please share it with others or leave a comment below. For more articles on chemistry and science, explore our website and discover the fascinating world of compounds and materials.
Cost To Install Septic Tank And Drainfield: A Comprehensive Guide
Pepsi Accident Jackson: A Deep Dive Into The Controversial Incident
Philly Cheesesteak Seasoning: The Ultimate Guide To Flavorful Steak
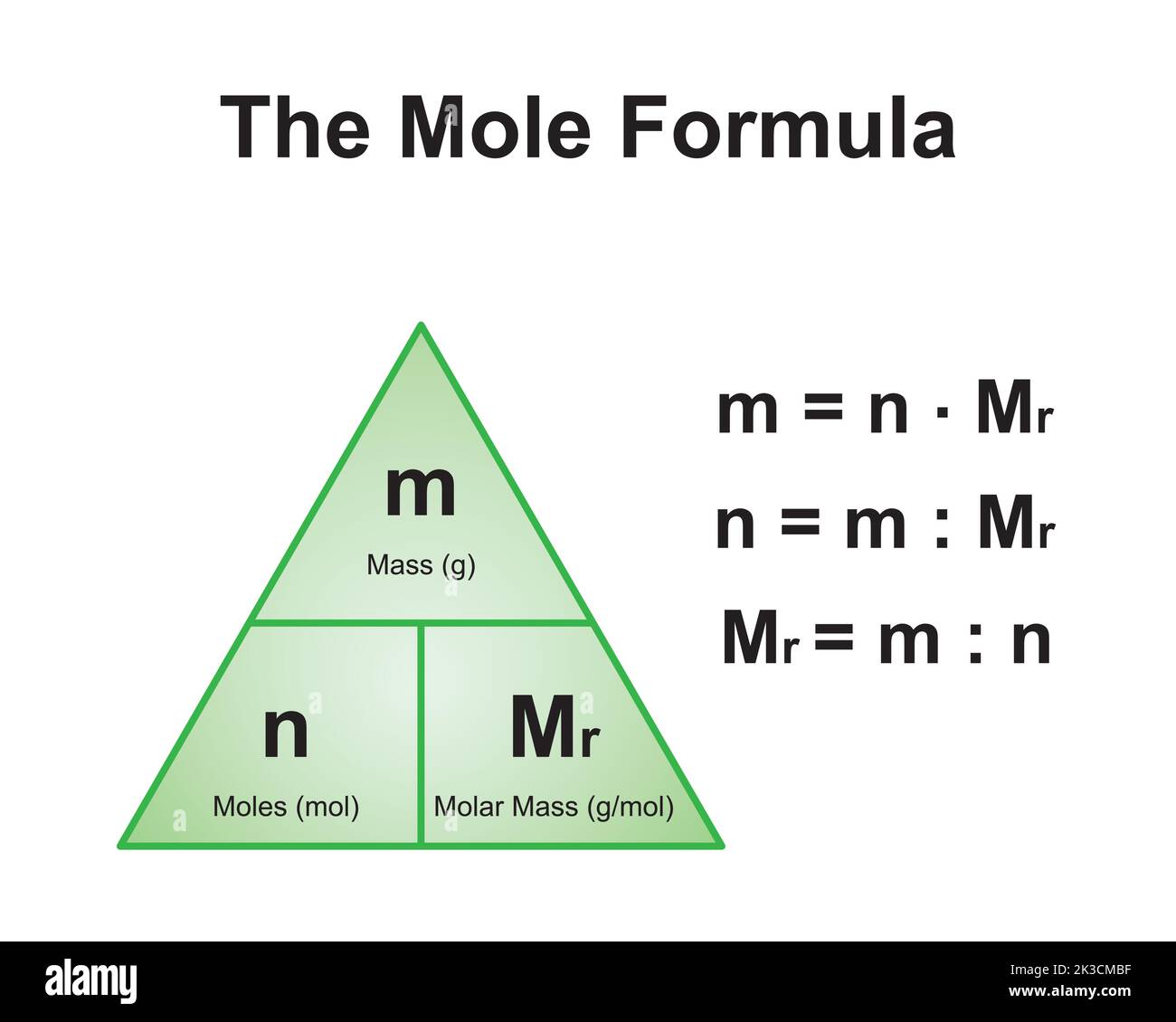
Scientific Designing of The Mole Formula Triangle. Relationship Between
Molar volume, illustration Stock Photo Alamy