Understanding The Formula Of Hypochlorous Acid: A Comprehensive Guide
Hypochlorous acid is a fascinating chemical compound with a wide range of applications, from disinfection to wound care. Its formula, HOCl, represents a simple yet powerful molecule that plays a crucial role in various industries. Understanding the formula of hypochlorous acid is essential for anyone interested in chemistry, healthcare, or environmental science. This article dives deep into the science behind hypochlorous acid, its properties, applications, and safety considerations.
Hypochlorous acid is a weak acid that forms when chlorine dissolves in water. It is widely recognized for its antimicrobial properties and is commonly used in disinfectants, sanitizers, and even as a natural defense mechanism in the human immune system. Despite its simplicity, this compound has a profound impact on modern life. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply curious about chemistry, this article will provide you with a thorough understanding of hypochlorous acid.
In the following sections, we will explore the chemical structure of hypochlorous acid, its role in various applications, and how it compares to other chlorine-based compounds. We will also discuss its safety, environmental impact, and the latest research surrounding this remarkable molecule. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of hypochlorous acid and its significance in our daily lives.
Read also:Dynasty Cast 1981 A Deep Dive Into The Iconic Tv Series
Table of Contents
- Chemical Structure of Hypochlorous Acid
- Physical and Chemical Properties
- Applications of Hypochlorous Acid
- Hypochlorous Acid in Disinfection
- Role in Wound Care
- Comparison with Other Chlorine Compounds
- Safety and Handling Guidelines
- Environmental Impact
- Latest Research and Developments
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Chemical Structure of Hypochlorous Acid
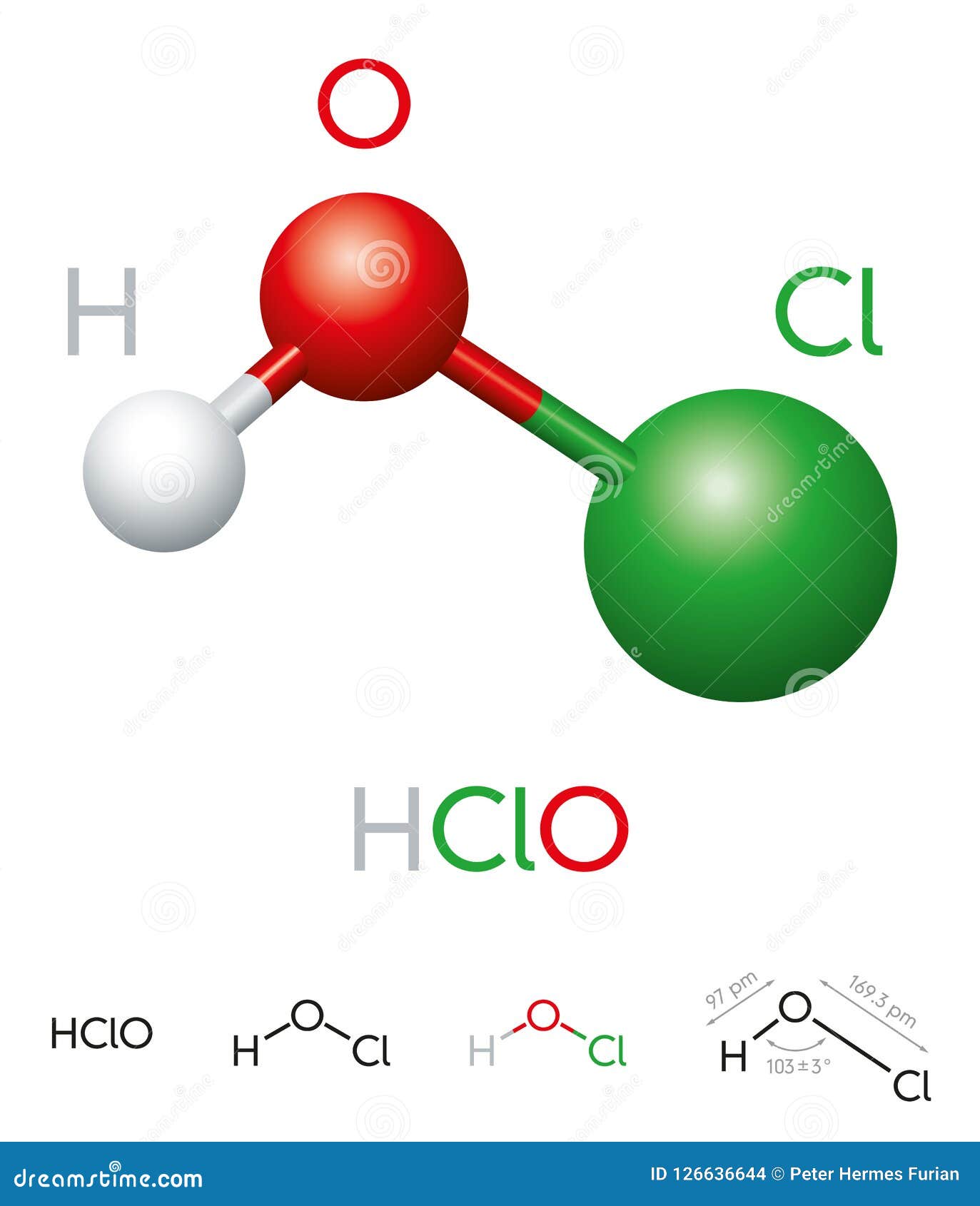
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is a simple molecule composed of one hydrogen (H) atom, one oxygen (O) atom, and one chlorine (Cl) atom. Its chemical formula, HOCl, indicates that it is a weak acid formed when chlorine gas dissolves in water. The structure of hypochlorous acid can be visualized as a central oxygen atom bonded to both hydrogen and chlorine atoms.
The bond between oxygen and chlorine is covalent, meaning that the electrons are shared between the two atoms. This bond is relatively weak, which is why hypochlorous acid is unstable and tends to dissociate into hypochlorite ions (OCl⁻) in solution. The dissociation process is pH-dependent, with more hypochlorite ions forming in alkaline conditions.
How Hypochlorous Acid Forms
Hypochlorous acid is typically generated through the reaction of chlorine gas (Cl₂) with water (H₂O). The chemical reaction can be represented as:
Cl₂ + H₂O → HOCl + HCl
This reaction produces both hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid (HCl). The equilibrium of this reaction is influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, and chlorine concentration. In practical applications, hypochlorous acid is often produced using electrolysis of a saltwater solution, which is a more controlled and sustainable method.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Hypochlorous acid is a colorless liquid with a slightly pungent odor. It is highly soluble in water and exhibits strong oxidizing properties, making it effective as a disinfectant. The compound is unstable and decomposes over time, especially when exposed to light, heat, or impurities.
Read also:Understanding The Zodiac Year 1965 Insights And Meanings
Key Properties of Hypochlorous Acid
- Oxidizing Power: Hypochlorous acid is a powerful oxidizing agent, capable of breaking down organic materials and killing microorganisms.
- pH Sensitivity: Its effectiveness depends on the pH of the solution. At lower pH levels, more hypochlorous acid is present, enhancing its antimicrobial activity.
- Decomposition: Hypochlorous acid breaks down into harmless byproducts like oxygen and water, making it environmentally friendly.
These properties make hypochlorous acid a versatile compound with applications in healthcare, water treatment, and household cleaning.
Applications of Hypochlorous Acid
The formula of hypochlorous acid is the foundation of its widespread use across various industries. Its antimicrobial properties and environmental safety make it a preferred choice for disinfection and sanitization. Below, we explore some of the most common applications of hypochlorous acid.
Disinfection in Water Treatment
Hypochlorous acid is widely used in water treatment plants to disinfect drinking water and remove harmful pathogens. It is effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, ensuring safe and clean water for public consumption. Unlike other chlorine-based compounds, hypochlorous acid leaves minimal residue, making it ideal for this purpose.
Use in Household Cleaning Products
Many household cleaning products contain hypochlorous acid due to its ability to kill germs and remove stains. It is commonly found in surface cleaners, laundry detergents, and bathroom disinfectants. Its non-toxic nature and ease of use make it a popular choice for maintaining hygiene at home.
Hypochlorous Acid in Disinfection
One of the most significant applications of hypochlorous acid is in disinfection. Its ability to kill a wide range of microorganisms has made it indispensable in healthcare, food processing, and public sanitation. Let's delve deeper into how hypochlorous acid works as a disinfectant.
Mechanism of Action
Hypochlorous acid disrupts the cell walls and membranes of microorganisms, leading to their destruction. It oxidizes vital components such as proteins and nucleic acids, rendering the pathogens inactive. This mechanism is highly effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, making hypochlorous acid a broad-spectrum disinfectant.
Advantages Over Other Disinfectants
- Non-Toxic: Unlike bleach or alcohol-based disinfectants, hypochlorous acid is safe for use on skin and surfaces.
- Fast-Acting: It provides rapid disinfection, often within seconds or minutes.
- Eco-Friendly: Its decomposition into harmless byproducts minimizes environmental impact.
Role in Wound Care
Hypochlorous acid has gained attention in the medical field for its role in wound care. Its antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility make it an excellent choice for cleaning and treating wounds. Let's explore how hypochlorous acid is used in this context.
Applications in Wound Healing
Hypochlorous acid is used in wound irrigation solutions and topical sprays to clean wounds and prevent infections. It effectively removes debris, bacteria, and biofilms without causing irritation or damage to healthy tissue. This makes it particularly useful for chronic wounds, surgical incisions, and burns.
Benefits for Patients
- Pain Reduction: Hypochlorous acid reduces inflammation and promotes faster healing.
- Antimicrobial Action: It prevents infections, which are a common complication in wound care.
- Non-Irritating: Unlike traditional antiseptics, hypochlorous acid is gentle on the skin.
Comparison with Other Chlorine Compounds
While hypochlorous acid shares similarities with other chlorine-based compounds like sodium hypochlorite (bleach) and chlorine gas, it stands out due to its unique properties. Below, we compare hypochlorous acid with these compounds to highlight its advantages.
Hypochlorous Acid vs. Sodium Hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite, commonly known as bleach, is a strong disinfectant but can be harsh and corrosive. In contrast, hypochlorous acid is milder and safer for use on skin and sensitive surfaces. It also breaks down more quickly, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
Hypochlorous Acid vs. Chlorine Gas
Chlorine gas is highly toxic and requires careful handling, making it unsuitable for many applications. Hypochlorous acid, on the other hand, is much safer and easier to use, especially in settings like healthcare and food processing.
Safety and Handling Guidelines
While hypochlorous acid is generally safe, proper handling is essential to ensure its effectiveness and prevent accidents. Below are some guidelines for using hypochlorous acid safely.
Storage Recommendations
- Store in a cool, dark place to prevent decomposition.
- Use opaque containers to protect the solution from light.
- Label containers clearly to avoid confusion with other chemicals.
Handling Precautions
- Wear gloves and protective eyewear when handling concentrated solutions.
- Avoid mixing hypochlorous acid with other chemicals, as this can produce harmful byproducts.
- Follow manufacturer instructions for dilution and application.
Environmental Impact
Hypochlorous acid is considered environmentally friendly due to its rapid decomposition into harmless byproducts like oxygen and water. Unlike other disinfectants, it does not contribute to long-term pollution or harm aquatic life. However, proper disposal is still necessary to minimize any potential impact.
Biodegradability
Hypochlorous acid breaks down quickly in the environment, leaving no toxic residues. This makes it an excellent choice for applications where environmental safety is a priority, such as in agriculture and water treatment.
Latest Research and Developments
Recent research has focused on enhancing the stability and efficacy of hypochlorous acid. Scientists are exploring new methods of production and stabilization to extend its shelf life and broaden its applications. Additionally, studies are investigating its potential use in advanced medical treatments and sustainable cleaning technologies.
Emerging Applications
- Use in air purification systems to eliminate airborne pathogens.
- Development of hypochlorous acid-based personal care products.
- Integration into smart home devices for automated disinfection.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, hypochlorous acid is a remarkable compound with a simple formula but profound applications. Its effectiveness as a disinfectant, its role in wound care, and its environmental safety make it a valuable tool in various industries. By understanding the formula of hypochlorous acid and its properties, we can harness its potential to improve health, hygiene, and sustainability.
We encourage you to share your thoughts or experiences with hypochlorous acid in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. For more insights into chemistry and its applications, explore our other articles on related topics.
Doraemon Weight: Unveiling The Curious Case Of The Beloved Robot Cat's Weight
Doraemon First Episode: A Journey Into The Iconic Beginning Of A Timeless Series
How Old Are The Kids In Little Rascals: A Comprehensive Guide
HClO Hypochlorous Acid Molecule Model and Chemical Formula Stock Vector

MJ6001 Hypochlorous Acid bactericide RAYMOND